- Home
- History of India
- Paleolithic Age
Paleolithic Age
Updated on 10-03-2022
Paleolithic age:
Paleolithic period is a prehistoric period of human activity who used stone as weapons and tools. Paleolithic men were hunter gatherers. “Paleo” means old and “lithic” means stone. The Paleolithic Age in India is divided into three phases in accordance with the type of stone tools used by the people and also according to the nature of climatic change.
The first phase is called Early or Lower Paleolithic, the second Middle Paleolithic, and the third Upper Paleolithic.
The oldest recognisable tools made by Paleolithic people were stone choppers such as those discovered at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. The prehistory of India goes back to the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic). While India lies at the eastern part, there are numerous Acheulean (relating to typical lower Paleolithic culture of middle Pleistocene Epoch characterised by large hand axes and clevers ) spots like Hathnora, in the Narmada Valley.
The broken skull specimen of Homo erectus is the first and only of its kind discovered in India so far of Paleolithic Age. This skull was discovered on 5th December, 1982 in the middle of the Narmada valley in Hathnora, Madhya Pradesh.
It is the most ancient human remnant so far discovered in Indian subcontinent. It was discovered in-situ which allows a precise determination of its stratigraphic, paleontological and cultural context that is clearly attributable to the Middle Pleistocene (around 500,000 years ago) age in the geological time scale.
This age covers
one of the longest time span as well as represent major climatic changes occurred
during this period.
Lower Palaeolithic Age
Lower Paleolithic Age
The early Stone Age may have begun in Africa around 2 million years ago but in India it began much earlier than in Africa and is expected to have occurred 600,000 million years ago. One of such oldest sites is located in Maharashtra at Bori.
The hunting and gathering was usually dependent mainly on the seasons. The vegetation also varied according to the season. During this period people were not aware of cooking and fire. People of lower Paleolithic Age ate all food in raw condition without being cooked as the fire was not known to them. These people were wanderers and hence moved from one place to another in search of food.
Read more about the History of India, Rajasthan and Delhi
Early old Stone Age excavation have been found in places like valley of river Son or Shown in Punjab, now in Pakistan. Several sites have been found in Kashmir and Thar Desert.
The tools have been also been excavated in places like Belan valley in UP and in certain parts of deserts of Rajasthan like Didwana.
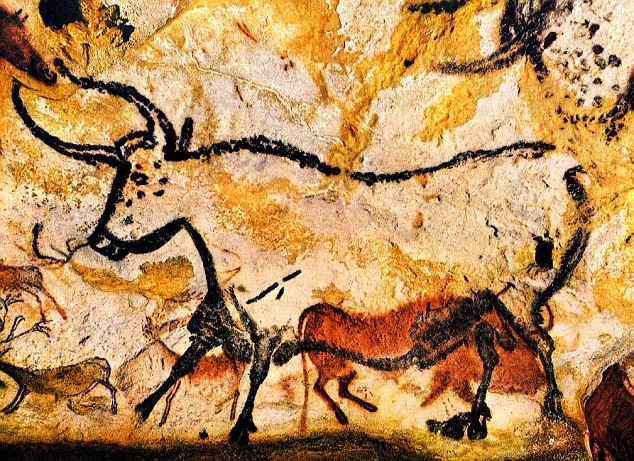
Other places where the traces of early Stone Age were found are Nagajunkunda in AP, caves and rock shelters in Bhimbetka near Bhopal. Rock paintings and carvings have been founded in Bhimbetka from different periods.
You can also read about
The animals that are carved in these paintings are mostly bison, elephants, tigers, rhino, boars etc. As on today about 750 caves have been discovered in Bhimbetka where such paintings are found.
The cave paintings on the rocks makes one wonder that if the animals themselves evolved out of these paintings or were people were better artists.
The paintings also showed the child birth, community dancing, drinking, religious rites, burials etc. The usual colours used were red and white with occasional colour of green and yellow. The themes were usually of everyday activities like hunting, dancing, masking, household scenes.
All the breath taking paintings that they have survived the time and weather till now demonstrate skills of people of Paleolithic Age.
Different Cultures in Palaeolithic Age
Read Culture of India and Rajasthan
During the lower Paleolithic era various culture and traditions can be observed.
Sohan culture
This culture prevailed during lower Paleolithic period in Pakistan. It was in 1928 where tools were discovered by Dr D.N. Wadia and Dr Helmet de Terra. Extensive pebbles and flakes are found in this area.
Madrasain culture
Mr Robert Bruce foot found hand axes near Chennai and called it as madrasain culture.
Acheulian culture
This is one of the longest cultures of the Paleolithic people. They are found in the terrace gravel of the Somme. This culture was named after a French site of Acheulean of the Indian subcontinent.
Most of the sites in India include Rajasthan, Deccan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, east and north east have been categorised in a]Acheulian culture.
In general this culture can
be divided into lower middle and upper culture. This culture continued
basically with bifacial core tools and primarily focused on hand axe. The hand
axes marked with sinuous edge. The lower Paleolithic people slowly started to
give way to Middle Paleolithic Age
Middle Paleolithic Age
Middle Paleolithic Age:
People of middle Paleolithic age started using more sophisticated tools during this period . The tools became more sharp and neat. The core tools completely changed into flake tools in this Age.
Both Levalloisian and Mousterian culture was developed on the flake tool tradition involving higher technology. Levalloisian culture which was started in the name of Porto Mousterian began in the middle Acheulean stage.
With the advent of flake tools this era is also called as flake tool age. While quartile, Quartz and basalt still continued to be used, many tools was replaced or supplemented by siliceous Rock. Important place in India of middle Paleolithic are Didwana Buddha Puskar in Rajasthan, valleys of the Belan, Son river Narmada River, Deccan plateau and Eastern Ghats.
Several activities such as catching large fish and hunting large
animals with specialised tools increased along with more elaborate social
organisation. It is believed that inter group trade of commodities such as raw
materials and other resources began in Middle Paleolithic age.
It is also believed and understood that people in Middle
Paleolithic age lived in groups mainly to distribute the food and resources to
have a continuous food supply. In the Middle Paleolithic period women gathered
plants and fire woods while men did hunting of animals for food.
Middle Paleolithic people used a technique known as ‘prepared core technique’ that was much better than the Acheulean technique.
The core artefacts were divided into two different parts known as formal cores and expedient cores. Each type had different work to do this helped middle Paleolithic people to create stone tipped spears and also sharp pointing stone flakes.
One of
the groups of middle Paleolithic age namely Neandertals believed to have
hunted large and big animals using these weapons. Use of fire became for
important for cooking food and for other purpose.
Upper Paleolithic Age
Upper Paleolithic age:
The upper Paleolithic age shows more specialised tools made on blades of the hand axes and flake tools of earlier periods. In this not only flint and similar rocks were used but also ivory and antler were also used.
One of the important discovery was the eggs of ostrich shells at over 40 sites in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra which shows that ostrich is a bird which adjusted to different climates was widely present in western part of India. During later part of Pleistocene due to climate change, vegetation became sparse.
The tools were further refined in upper paleolithic period. The refined tools are evident from the bores in stones grinding slabs etc. The bored stones are still used by fisherman as net sinkers in fishing and marine fishing. Some of the important places of Paleolithic sites in India are Lidder river in Pahalgham currently in Jammu and Kashmir (India), Sohan valley in Punjab (India), Belan valley river, Ghataprabha river in Karnataka, Attirpakkam in Tamil Nadu.
Due to harsh and
arid climate the vegetation was sparse. The fossils of flora and fauna show the
presence of grass land. The tools of the upper paleolithic people were made by
blade and they showed a marked regional diversity with respect to refinement of
the tools and standardisation of finished tools.
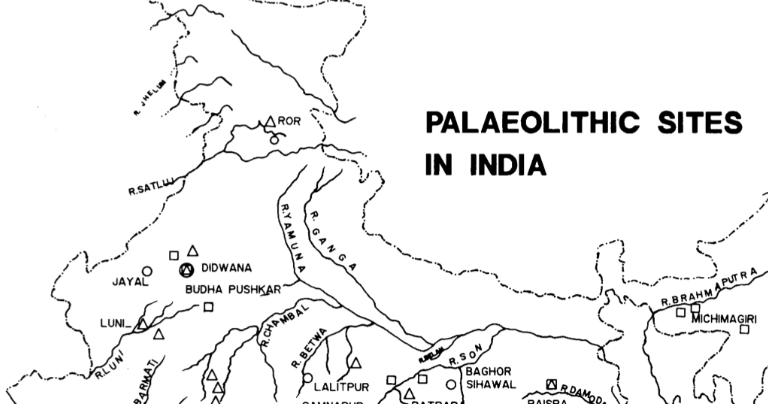
Paleolithic Sites in India
Here is a list of some of the important Palaeolithic sites in India.
Bori in Maharashtra
Sohan in Punjab (now in Pakistan)
Belan Valley in Uttar Pradesh
Desert area of Didwana in Rajasthan
Chirki- Nevasa in Maharastra
Narmada Valley in Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Gujarat
Sabarmati Valley in Gujarat.
Nagarjunakonda in Andhra Pradesh.
Caves and rock shelters in Bhimbetka near Bhopal.
Places near River Narmada and Tungabhadra River
Belan Valley in Madhya Pradesh
Ghataprabha River in Karnataka
Hunsgi in Gulbarga Karnataka
Attirampakkam in Tamil Nadu.
Pahalgham in Kashmir.
Singhbhum in Jharkhand.
Tools used in Paleolithic Period
Paleolithic people made tools from stone, Bone and wood. They preferred to stay near water source because of the stone tools used by them.
The earliest stone tool industry in Oldowan (early stone tool archaeological
industry). These early tools were very simple and easy to make. They were just
chipped of few flakes of stones. Oldowan tools were mostly used during Lower Paleolithic period.
Some of the important lower Paleolithic tools include clever, Hand axe and Chopper. These tools were blunt and were easy to make.
It was easy to handle as well to hunt for food. It was used for cutting or digging and even for cleaning and skinning the prey.
The tools were made from quartize and also
basalt. These tools are found mainly near Narmada, Tapti River, Bhimbetka,
Didwan in Rajasthan and also near Krishna river.
Read some of the important pages
As the time progressed the Middle Paleolithic tools were more refined, thinner and lighter. Stones that were available during this period were comparatively small hence it was also known as microliths.
Basalt and
quartzite were used to make tools in middle Paleolithic period. Harpoons were
invented and were used in the late middle Paleolithic period. Due to the
invention of harpoons fish was included in the diet of the people.
The tools were further improved and refined in Upper Paleolithic period as compared to Lower and middle Paleolithic period. The tools were scrappers, blades and burins. With the development in the technology significant development on tools were seen. Improved blades from industries were replaced for flake blades and Burins and racloirs were used for bone or hide (skin of animal) and antler.
Since hunting became an
important occupation these tools gained prominence. The improvement in the
tools is evident from the holes in the stones and grinding slabs. Primarily Paleolithic people used hand axes as a very important tool for hunting.
Update on coronavirus in India
Affiliate Disclosure:
If you make any purchase via a link on this site, I may receive a small commission with no added cost to you.